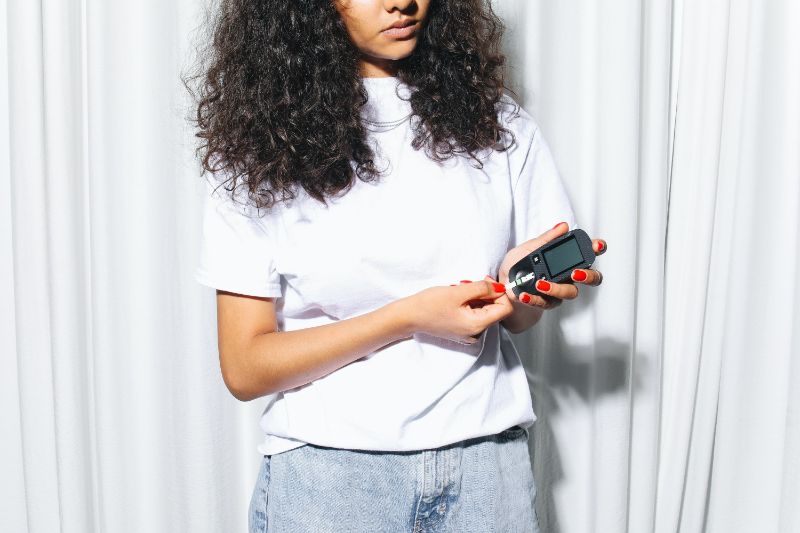
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels and affecting millions of people worldwide. There are three types of diabetes, Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.
When you choose Grand Forks Clinic, you can expect personalized and patient-centered care. We believe in treating the whole person, addressing not only the physical aspects of diabetes but also the emotional and psychological well-being of our patients.
Our comprehensive diabetes care services are designed to meet your unique needs and help you navigate the complexities of diabetes management with confidence.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when the pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin or the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, helping to control blood sugar levels. When there is inadequate insulin production or improper utilization by the body, it leads to a buildup of glucose in the bloodstream, resulting in high blood sugar levels, also known as hyperglycemia or diabetes.
Consistently high blood glucose levels can contribute to various health complications, including heart disease, nerve damage, kidney problems, and vision issues. It is essential to address diabetes to maintain overall well-being.
There are various types of diabetes, but the most common forms include:
- Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is the most prevalent type, often developing in adulthood, although it can affect people of all ages. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or does not produce enough insulin to control blood sugar levels effectively.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes, or insulin-dependent diabetes, typically begins in childhood or early adulthood. It is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Patients with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy.
- Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth. However, women who develop gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Diabetes manifests through various symptoms that can vary in intensity and presentation. Some common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Excessive thirst (polydipsia)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Increased hunger (polyphagia)
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Numbness and tingling
In some cases, diabetes may not present any symptoms, particularly in the early stages of the condition. Therefore, regular check-ups and screenings are essential for early detection and effective management of diabetes.
Diabetes is a complex condition with multiple factors contributing to its development. Understanding these causes can provide insight into the management and prevention of diabetes.
At Grand Forks Clinic, we prioritize educating our patients about the different factors that play a role in diabetes onset. Let's explore the key causes in more detail.
Insufficient Insulin Production
In some cases, diabetes occurs when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Insulin is responsible for transporting glucose from the bloodstream into cells, where it is used as a source of energy.
When insulin production is insufficient, blood sugar levels can rise, leading to diabetes.
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is another common cause of diabetes. It occurs when the body's cells become resistant to the effects of insulin and are unable to utilize it efficiently.
As a result, the pancreas produces more insulin in an attempt to compensate, but it eventually becomes overwhelmed, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics plays a significant role in diabetes risk. People with a family history of diabetes are more likely to develop the condition. Although genetics alone may not cause diabetes, it can increase your susceptibility to other risk factors, such as obesity or an unhealthy lifestyle.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices can significantly impact diabetes development. Sedentary lifestyles, poor dietary habits, and excessive weight gain increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Consuming processed foods high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance over time. Regular physical activity and a balanced diet are essential in preventing and managing diabetes.
Gestational Factors
Gestational diabetes affects pregnant women and is characterized by high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Hormonal changes can interfere with the body's insulin production and utilization, leading to gestational diabetes.
It is crucial to manage gestational diabetes to protect the health of both the mother and the baby. Women with gestational diabetes also have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Other Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can contribute to diabetes development. For example, conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which affects hormone levels in women, can increase the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Additionally, certain medications, such as corticosteroids or antipsychotics, can disrupt insulin production or utilization, leading to diabetes.
Diagnosing diabetes involves evaluating blood glucose levels through specific tests that provide valuable insights into your condition.
Fasting Blood Glucose Test
A fasting blood glucose test is one of the most common tests used to diagnose diabetes. This test measures your blood sugar levels after a period of fasting, usually overnight.
During the test, a sample of your blood is taken and analyzed to determine the amount of glucose present. A fasting blood glucose level of 126 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or higher on two separate occasions is indicative of diabetes.
Random Blood Glucose Test
A random blood glucose test is another method used to diagnose diabetes. This test measures your blood sugar levels at any time of the day, regardless of when you last ate.
It is particularly useful in detecting diabetes when you are experiencing symptoms such as increased thirst or frequent urination.
A random blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher, accompanied by symptoms of diabetes, suggests the presence of the condition.
A1c Test
The A1c test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, provides a comprehensive picture of your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It measures the percentage of hemoglobin in your blood that is coated with glucose.
The results are presented as a percentage, with higher percentages indicating elevated blood sugar levels. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher on two separate tests is considered diagnostic for diabetes.
It is important to note that these tests are not used in isolation but in combination with a thorough evaluation of your medical history, symptoms, and risk factors. Our healthcare professionals at Grand Forks Clinic take a holistic approach to diagnosis, considering all relevant factors to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
At Grand Forks Clinic, we understand the challenges of managing diabetes and are here to support you every step of the way. Our expert team will provide you with individualized care and help you develop a personalized treatment plan to address your specific needs.
Our approach may include:
- Personalized treatment plans tailored to your unique needs
- Prescription medications and insulin therapy
- Guidance on nutrition, exercise, and stress management
- Education on blood sugar monitoring
- Ongoing support and education
Don't let diabetes hold you back. Take charge of your health and schedule a consultation with one of our skilled practitioners at Grand Forks Clinic by calling us at (701) 775-5800 or requesting an appointment online.
We are here to help you achieve optimal health and improve your quality of life.